Ad Code
Featured Section
Article épinglé
Formulaire de contact
Consultations de pages
Step Recovery Diode: Generating Short Pulses for Microwave Electronics
A step recovery diode is a semiconductor junction diode that has unique features useful for microwave electronics. One of its primary applications is generating harmonics in low power multipliers with output frequencies of up to 5 GHz. It does this by storing a charge as the diode is driven to forward conductance by the positive voltage of the input signal.
The step recovery diode's ability to generate extremely short pulses and its unusual doping profile with a concentration of charge carriers decreasing near the junction, which causes a phenomenon called the reverse snap-off, allows it to generate sharp pulses useful for pulse generation circuits. It also has a very fast recovery time, which allows it to handle high peak currents and voltages.
Due to these unique features, step recovery diodes are used in voltage-controlled oscillators, frequency synthesizers, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input. They are also useful in pulse generators and parametric amplifiers.
In summary, the step recovery diode is a specialized diode that generates short pulses and is useful in various applications in microwave electronics, including pulse generation, harmonics, voltage-controlled oscillators, and parametric amplifiers.
Step recovery diode
A step recovery diode is a type of diode that is used as a harmonic generator in low power multipliers with output frequencies of up to 5 GHz
. It generates harmonics by storing a charge as the diode is driven to forward conductance by the positive voltage of the input signal. The ability of step recovery diodes to generate sharp pulses makes them useful in voltage-controlled oscillators, frequency synthesizers, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input
. They feature fully passivated, true mesa construction for sharp transitions and improved stability, and have the industry's fastest transition times for millimeter wave multiplication and picosecond pulse forming
. They are used in waveguide, coaxial, and stripline applications
What is a step recovery diode used for
Step recovery diodes are used for generating harmonics in low power multipliers with output frequencies of up to 5 GHz
. They generate sharp pulses, making them useful in voltage-controlled oscillators, frequency synthesizers, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input
. They feature fully passivated, true mesa construction for sharp transitions and improved stability, and have the industry's fastest transition times for millimeter wave multiplication and picosecond pulse forming
. They are used in waveguide, coaxial, and stripline applications
. In summary, step recovery diodes are used for generating harmonics, voltage-controlled oscillators, frequency synthesizers, and comb generators.
What is a step recovery diode and how does it work
A step recovery diode is a type of semiconductor junction diode that has the ability to generate extremely short pulses. It is also known as a snap-off diode, charge-storage diode, or memory varactor. It is a voltage-dependent variable capacitor diode with an unusual doping profile that provides maximum switching speed at low frequency. The diode features a very fast recovery time, which allows it to handle high peak currents and voltages. When the diode is driven to forward conductance by the positive voltage of the input signal, it generates harmonics by storing a charge. When the signal reverses polarity, this charge is extracted, causing a voltage pulse to form in the impulse circuit of the multiplier. Step recovery diodes are used in microwave electronics as pulse generators or parametric amplifiers
What is the unique feature of a step recovery diode
The unique feature of a step recovery diode is its ability to generate extremely short pulses due to its abrupt switching from forward conduction to reverse cut-off
. When diodes switch from forward conduction to reverse cut-off, a reverse current flows briefly as stored charge is removed. It is the abruptness with which this reverse current ceases which characterizes the step recovery diode
. The diode has an unusual doping profile with a concentration of charge carriers decreasing near the junction, which causes a phenomenon called the reverse snap-off
. This diode acts like a normal diode in forward bias and blocks current in reverse bias, but when switched from forward to reverse bias by a high-frequency signal, it does not recover immediately, which takes some time to drain away from the junction
. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
.What is the difference between a step recovery diode and a normal diode
The main difference between a step recovery diode and a normal diode is their operating principle. A normal diode conducts in the forward direction and blocks current in the reverse direction. However, a step recovery diode operates as an ordinary diode at low frequency, i.e., it conducts in the forward direction but not in the reverse direction, or it recovers immediately from ON state to OFF state. But when driven forward-to-reverse by a high-frequency signal, it does not recover immediately, which takes some time to drain away from the junction. It looks as though the diode has suddenly snapped open during the early part of the reverse cycle. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
. In summary, the main difference between a step recovery diode and a normal diode is their ability to generate extremely short pulses and their unusual doping profile, which provides maximum switching speed at low frequency
What are the applications of a step recovery diode
Step recovery diodes have a variety of applications in microwave electronics as pulse generators or parametric amplifiers
. They are used for repetitively pulsed operation, as they feature a very fast recovery time, which allows them to handle high peak currents and voltages
. They are also called peak current diodes or avalanche diodes
. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
. Because of this, step recovery diodes are useful in frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input
. They are also used in waveguide, coaxial, and stripline applications
. In summary, step recovery diodes are used in pulse generators, parametric amplifiers, frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators.
What are the advantages of using a step recovery diode over other diodes
The advantages of using a step recovery diode over other diodes include its ability to produce sharp pulses that are useful for pulse generation circuits
. It has a very fast recovery time, which allows it to handle high peak currents and voltages
. The diode produces a snap-off current that is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
. This makes it useful in frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input
. The diode has an unusual doping profile that provides maximum switching speed at low frequency
. In summary, the advantages of using a step recovery diode over other diodes include its ability to produce sharp pulses, fast recovery time, and rich harmonics, making it useful in various applications such as pulse generation circuits, frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators.
How does the reverse snap-off phenomenon work in step recovery diode
The reverse snap-off phenomenon in a step recovery diode occurs when the diode is switched from forward to reverse bias by a high-frequency signal. When the diode is forward biased, it conducts, and in reverse biased condition, it acts as an open circuit. However, when it is switched from forward to reverse bias, it instantly changes its state from ON to OFF. But it takes some time to drain away from the junction, which looks as though the diode has suddenly snapped open during the early part of the reverse cycle. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
. The diode has a concentration of charge carriers decreasing near the junction, which causes the reverse snap-off phenomenon
. The reverse snap-off phenomenon is responsible for the diode's ability to generate extremely short pulses, making it useful in pulse generation circuits
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using step recovery diode
The advantages of using a step recovery diode include high forward current, fast switching time, and sharp harmonics, making it useful in pulse generation circuits, frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators
. The diode has a very fast recovery time, which allows it to handle high peak currents and voltages
. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency
. However, the disadvantages of using a step recovery diode include its high cost compared to other diodes and its sensitivity to temperature changes
. The diode has an unusual doping profile that provides maximum switching speed at low frequency, but this also makes it sensitive to temperature changes
. In summary, the advantages of using a step recovery diode include its ability to produce sharp pulses, fast recovery time, and rich harmonics, while its disadvantages include high cost and sensitivity to temperature changes.
What is the difference between a step recovery diode and a PIN diode
The main difference between a step recovery diode and a PIN diode is their operating principle. A PIN diode is a three-layer diode with a p-type layer sandwiched between two n-type layers. It has a wide intrinsic region that acts as a resistor when forward-biased and as a capacitor when reverse-biased. It is used as a variable resistor or attenuator in RF and microwave circuits. On the other hand, a step recovery diode operates as an ordinary diode at low frequency, i.e., it conducts in the forward direction but not in the reverse direction, or it recovers immediately from ON state to OFF state. But when driven forward-to-reverse by a high-frequency signal, it does not recover immediately, which takes some time to drain away from the junction. It looks as though the diode has suddenly snapped open during the early part of the reverse cycle. The snap-off current of a step-recovery diode is rich in harmonics and can be filtered to give a sinusoidal wave of a higher frequency. Because of this, step recovery diodes are useful in frequency synthesizers, voltage-controlled oscillators, and comb generators for generating multiple harmonics of their input
Rechercher
Categories
Popular Posts
montage amplificateur inverseur
Carte d’extension I2C 64 I/O pour RaspberryPi

schema électrique autoradio

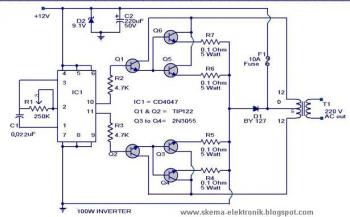
Onduleur 100 Watt 12V DC à 220V AC

Hauteur interrupteur lit











0 Commentaires