Ad Code
Featured Section
Article épinglé
Formulaire de contact
Consultations de pages
The Bright Side of Science: How LED Lights Work ?
Have you ever wondered how those tiny little diodes in your LED light bulb magically light up your room? Let’s dive into the science of LED lights and shed some light on this illuminating topic.
LED stands for Light Emitting Diodes – which may sound like a mouthful but really just means that they emit light when electricity passes through them. So how do they do it? Well, it all starts with a positive and negative semiconductor material. When voltage is applied to these materials, electrons start flowing from one side to the other, releasing energy in the form of light.
But wait, there’s more! Traditional light bulbs generate a lot of heat as a byproduct when they produce light. LEDs, on the other hand, are way more energy efficient and only produce a fraction of the heat. This means that you can keep your LED lights on for hours without worrying about scorching your hands when you change the bulb.
Another cool thing about LED lights is that they come in a variety of colors. This is because the semiconductor material can be altered to make different colors when electricity is applied. It’s like a light show right in your own home!
So if LEDs are so great, why aren’t they used for everything? Well, LEDs aren’t great for lighting up large areas, like a stadium or an outdoor parking lot. They also need a little more setup than traditional light bulbs. But for small spaces, like your desk or your living room, they are the way to go.
Now that you understand the science of LED lights, you can appreciate the bright side of science – pun intended. It’s amazing how such a tiny diode can emit so much light while being energy efficient and long-lasting. So the next time you turn on your LED lights, you can impress your friends with your newfound knowledge.
Rechercher
Categories
Popular Posts

schema électrique autoradio

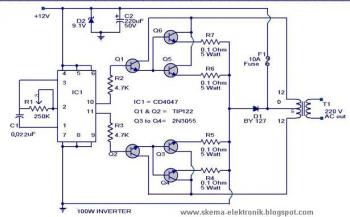
Onduleur 100 Watt 12V DC à 220V AC

Hauteur interrupteur lit

schema électrique autoradio







0 Commentaires